DMARC record is more important than ever with the latest Gmail update. Are you concerned about spammers attempting to fake your email domain for fraudulent activities?
If you are wondering whether your emails consistently land in the intended inboxes or not, then you need a DMARC record. DMARC stands for Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance. This email security measure holds the key to resolving email phishing and spoofing.
Today, in this guide, we will get an in-depth understanding of what Is DMARC record, why you need it, and how to implement a DMARC record for email security and delivery. Let's dive into the details.
What is DMARC?
DMARC is an email authentication protocol to safeguard a domain from unauthorized uses like email spoofing. In simple words, it’s a way to authenticate email messages. The full form of DMARC is Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance.
Email spoofing often leads to phishing attacks. DMARC allows domain owners to publish policies in their DNS records. There are authentication mechanisms like SPF and DKIM. This provides a mechanism for receiving reports on messages that either pass or fail the DMARC test.
3 Types of DMARC Policies
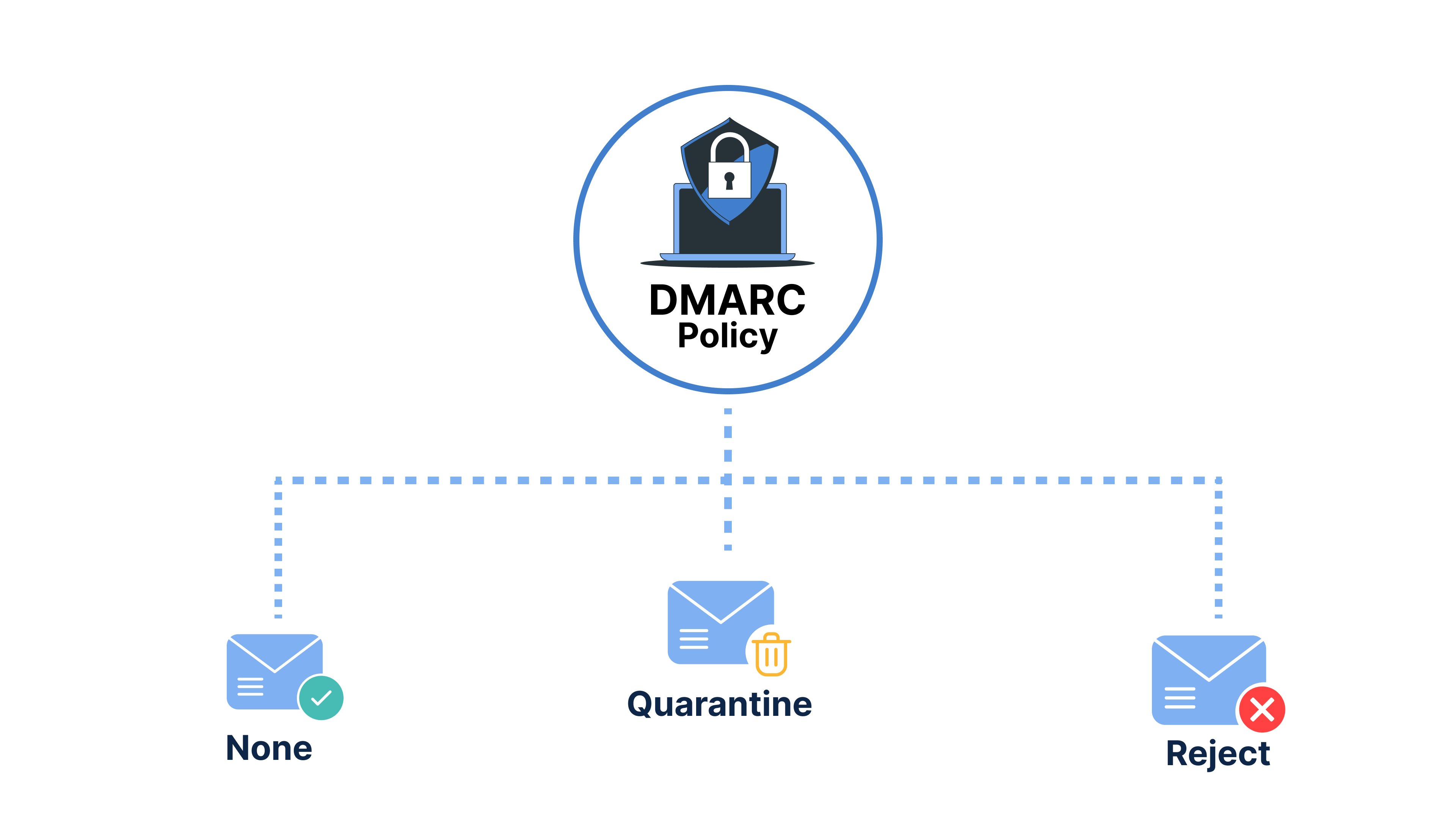
A DMARC policy provides instructions for an email receiver on addressing messages that do not pass authentication checks. There are three types of DMARC Policies:
None (p=none):
This policy type is often used during the initial implementation of DMARC. It allows domain owners to monitor email traffic without taking any immediate action based on the DMARC results.
Action to Take: No enforcement action is applied. The email receiver may send DMARC reports to the specified email address, allowing the domain owner to analyze and understand how their domain is being used for email authentication.
Example: v=DMARC1; p=none; rua= mailto:(email address);
Quarantine (p=quarantine):
This policy is a step up in terms of enforcement. When an email fails DMARC authentication, it may be marked as suspicious and sent to the recipient's spam or quarantine folder. This helps protect users from potentially malicious emails while still allowing the domain owner to monitor the impact on legitimate email traffic.
Action to Take: Suspicious emails are moved to the recipient's spam or quarantine folder, providing an extra layer of protection against phishing attempts.
Example: v=DMARC1; p=quarantine; rua= mailto:(email address);
Reject (p=reject):
This is the most stringent DMARC policy. When an email fails DMARC authentication, it is outright rejected, and the recipient's mail server does not deliver it to the inbox or any other folder. This policy provides the highest level of protection against unauthorized use of a domain and helps prevent phishing attacks.
Action to Take: Emails that fail DMARC authentication are rejected, and the recipient is not delivered to the recipient's inbox.
Example: v=DMARC1; p=reject; rua= mailto:(email address);
Note: Adopting a DMARC policy set to "reject" substantially reduces the possibility of domain abuse, phishing, and spoofing attacks.
What is DMARC Record?
DMARC record is one of the most important elements of email security. DMARC policies are kept in the DNS TXT records. Usually, DNS TXT records are kept as text records that are associated with a domain. Let's see an example of a DMARC record:
The DMARC record includes various values depending on the version of DMARC used. The action will be taken for failed messages the percentage of messages subject to DMARC evaluation, and more.
DMARC Record Tags
Why Do You Need a DMARC Record
A DMARC record is a crucial component of Email authentication, and it serves several important purposes.
1. Email Authentication
DMARC helps protect email recipients from phishing and email spoofing attacks. By using authentication mechanisms like SPF (Sender Policy Framework) and DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail), DMARC allows domain owners to verify that the emails sent on their behalf are legitimate.
2. Prevent Email Spoofing by Sender Policy Framework (SPF)
SPF is a component of DMARC that specifies which mail servers are authorized to send emails on behalf of a particular domain. The DMARC record includes information about SPF, helping to prevent unauthorized sources from sending emails using a domain.
3. Reduce Phishing and Cyberattacks by DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM)
DMARC significantly reduces the risk of phishing and cyberattacks. DKIM is another authentication mechanism used by DMARC. It involves the use of cryptographic signatures to verify that an email message was sent by the claimed sender.
4. Increased Email Deliverability
Implementing DMARC can significantly enhance email deliverability. By providing a mechanism for email receivers to verify the authenticity of emails sent on behalf of a domain, it increases email deliverability. A DMARC-recorded authenticated email is more likely to reach the intended recipients' inboxes.
5. DMARC Reporting
DMARC provides an option for email receivers to send feedback (DMARC reports) to domain owners. This reporting helps domain owners monitor email traffic, identify potential issues, and take corrective actions.
6. Policy Enforcement
DMARC allows domain owners to specify a policy for handling emails that fail authentication checks. There exist three DMARC policy choices: None (Monitoring Only), Quarantine, and Reject. This policy can instruct email receivers to deliver, quarantine, or reject messages that don't meet the specified authentication criteria. This helps in reducing the likelihood of fraudulent emails reaching recipients.
By implementing DMARC and publishing a DMARC record, domain owners can enhance the security of their email. Now let’s know the ways to implement DMARC records into your domain.
To begin, give the details of your domain, sender name, email, and reply email. Click the Save button and the values in the records table above will get automatically filled.
How to Implement a DMARC Record
You can implement a DMARC record by following the below steps.
1. Go to your DNS Hosting Provider:
Proceed to your DNS hosting provider, and log in. Keep in mind that interfaces differ across different hosting providers.
2. Set Up SPF and DKIM:
Build on existing email authentication methods by setting up SPF and DKIM.
3. Generate Your DMARC Record
Go to the option to create a new record or access the TXT section for editing. You can also use DMARC generators to create your record for DMARC for free.
4. Publish a DMARC Policy:
Now create a DMARC policy once SPF and DKIM are in place. Specify how email receivers should handle messages that fail DMARC evaluation and publish this policy in your domain's DNS records.
5. Monitor DMARC Reports:
After that, monitor DMARC reports to know how your domain's email is handled, including details on passing or failing messages.
6. Analyze DMARC Reports and Take Action:
Analyze DMARC reports to identify issues with email spoofing and take appropriate action. Once you have analyzed the reports, try to quarantine email sources that do not align with DMARC.
7. Monitor and Update Your DMARC Policy:
Continuously monitor the effectiveness of your DMARC policy. Make adjustments as needed to enhance email security and ensure ongoing protection against spoofing.
8. Keep DNS Records Up-to-Date:
Regularly update your DNS records to safeguard your email deliverability.
If you are an online course creator, you may need to handle a course site and send emails to your audience. There you will need to implement a DMARC record so that your emails are delivered properly.
We are using EzyCourse, the all-in-one online course platform where you can set up DMARC records.
How to Set a DMARC Record in EzyCourse
To set a DMARC record, you will be required to set up some options from the EzyCourse dashboard. Let’s know it step by step.
Step 1: Go to Marketing & Contacts > Email white label setting.
Step 2: Here, you’ll see several DNS record settings like this:
Step 3: Provide the details of your domain, sender name, email, and reply email. Click the Save button and the values in the records table above will be automatically filled.
Step 4: After that, log in to your domain registrar’s website and create the DNS records exactly as given on your EzyCourse dashboard (TXT, CNAME, TXT).
Step 5: Finally, you’ll get a Verification button on top of the records table after creating the records. Click on it to verify all the credentials. If everything is okay, the status will appear as a green Verified text.
And that’s all!
Frequently Asked Questions
What does a DMARC record do?
A DMARC record instructs email receivers on how to handle messages that fail DMARC evaluation. The DMARC record includes various values depending on the version of DMARC used. The action will be taken for failed messages the percentage of messages subject to DMARC evaluation, and more.
How does DMARC prevent email spoofing?
DMARC prevents email spoofing by authentication methods like SPF and DKIM. SPF is a component of DMARC that specifies which mail servers are authorized to send emails on behalf of a particular domain. DKIM is another authentication mechanism used by DMARC. It involves the use of cryptographic signatures to verify that an email message was sent by the claimed sender.
Is DMARC a one-time implementation?
No, DMARC is a continuous process that requires ongoing monitoring, maintenance, and updates. You have to adapt to the changes in email infrastructure to prevent security threats. DMARC record is an important tool in the fight against email phishing and spoofing.
Final Words
Overall, DMARC records are one of the most important methods to fight against email threats. By knowing what is DMARC and how to implement a DMARC record, you can strengthen your email security.
Hope this guide helped you. If you have any queries, feel free to reach out to us!